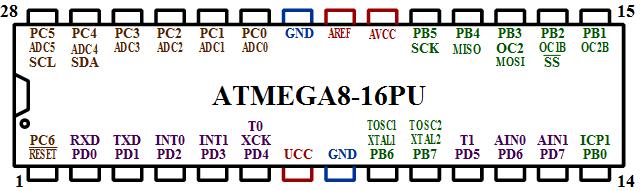
ATmega8 is an atmel’s low-power 8-bit AVR RISC-based microcontroller combines 8KB of programmable flash memory, 1KB of SRAM, 512K EEPROM, and a 6 or 8 channel 10-bit A/D converter. The device supports throughput of 16 MIPS at 16 MHz and operates between 2.7-5.5 volts.
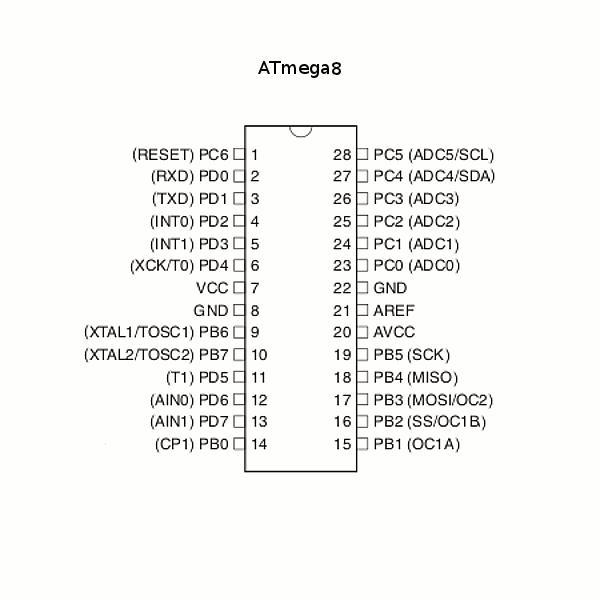
To find out its complete Specs, here is the link to ATmega8 datasheet , Under given is another view for its pin diagram.
Pin Descriptions
VCC Digital supply voltage.
GND Ground.
Port B (PB7..PB0)
XTAL1/XTAL2/TOSC1/
TOSC2
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Depending on the clock selection fuse settings, PB6 can be used as input to the inverting Oscillator
amplifier and input to the internal clock operating circuit.
Depending on the clock selection fuse settings, PB7 can be used as output from the inverting
Oscillator amplifier.
If the Internal Calibrated RC Oscillator is used as chip clock source, PB7..6 is used as TOSC2..1
input for the Asynchronous Timer/Counter2 if the AS2 bit in ASSR is set.
The various special features of Port B are elaborated in “Alternate Functions of Port B” on page
58 and “System Clock and Clock Options” on page 25.
Port C (PC5..PC0) Port C is an 7-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port C output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port C pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
PC6/RESET If the RSTDISBL Fuse is programmed, PC6 is used as an I/O pin. Note that the electrical characteristics
of PC6 differ from those of the other pins of Port C.
If the RSTDISBL Fuse is unprogrammed, PC6 is used as a Reset input. A low level on this pin
for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a Reset, even if the clock is not running.
The minimum pulse length is given in Table 15 on page 38. Shorter pulses are not guaranteed to
generate a Reset.
The various special features of Port C are elaborated on page 61.
Port D (PD7..PD0) Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port D output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port D pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port D also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega8 as listed on page
63.
RESET Reset input. A low level on this pin for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a
reset, even if the clock is not running. The minimum pulse length is given in Table 15 on page
38. Shorter pulses are not guaranteed to generate a reset.