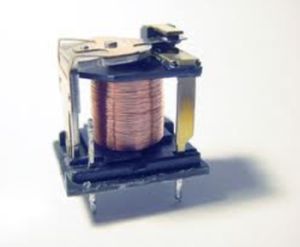
Relay Construction
Relays are amazingly simple devices. There are four parts in every relay:
- Electromagnet
- Armature that can be attracted by the electromagnet
- Spring
- Set of electrical contacts
The following figure shows these four parts in action:
In this figure, you can see that a relay consists of two separate and completely independent circuits. The first is at the bottom and drives the electromagnet. In this circuit, a switch is controlling power to the electromagnet. When the switch is on, the electromagnet is on, and it attracts the armature (blue). The armature is acting as a switch in the second circuit. When the electromagnet is energized, the armature completes the second circuit and the light is on. When the electromagnet is not energized, the spring pulls the armature away and the circuit is not complete. In that case, the light is dark.
When you purchase relays, you generally have control over several variables:
- The voltage and current that is needed to activate the armature
- The maximum voltage and current that can run through the armature and the armature contacts
- The number of armatures (generally one or two)
- The number of contacts for the armature (generally one or two — the relay shown here has two, one of which is unused)
- Whether the contact (if only one contact is provided) is normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC)
Relay Applications
In general, the point of a relay is to use a small amount of power in the electromagnet — coming, say, from a small dashboard switch or a low-power electronic circuit — to move an armature that is able to switch a much larger amount of power. For example, you might want the electromagnet to energize using 5 volts and 50 milliamps (250 milliwatts), while the armature can support 120V AC at 2 amps (240 watts).
For more detail: How Relays Work