Introduction
Approach used for creating the pure sine wave described in this paper is done
through manipulation of mathematical representation of the original sine wave. It is
done by dividing half the sine wave into m (even number) segmentations, where
area under a quarter of the sine wave from 0 to π/2 resembles series of the form
[2n-1] where n=1,…, m/2, while areas of the next quarter from π/2 to π will
resemble series of the form [2n-1] where n=m/2,.., 1.
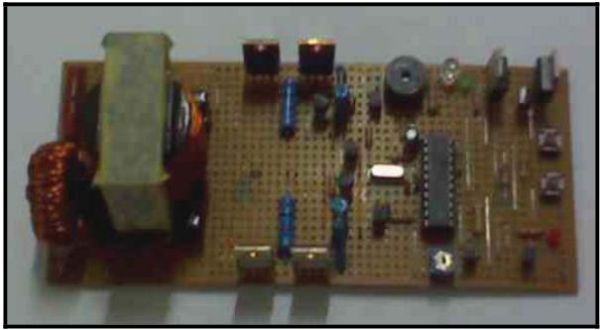
Block Diagram & Schematic
The inverter will converts 12 Volt dc from battery into 110 Volt ac, 50 Hz, sine
wave. Figure 2 and 3 show the block dagram and schemnatic circuit of the inverter.
Pulse train as shown in figures 5 is produced interchangeably from port (A)
and port (B) by microcontroller 89S2051 during the positive half and negative half of
the sine wave. The pulse train is then inputted to the MOSFET power switching
circuit, which is next directed to the primary side of the transformer. Output of the
secondary side is shown in Figure 6, which then be filtered resulting in the sine wave
as seen in figure 7, where amplitude attenuation can reach up to 50%. Measured
inverter output THD reaches 5-8%, where the largest harmonics appeared to be the
second and third harmonics as shown in figure 8.
For more detail: Mathematical Manipulation of Pure Sine Wave Inverter Using Atmel 89S2051