Summary of STEREO 64LEDS VU METER CIRCUIT ATMEGA8
This article describes the design and construction of a 2x32 LED VU meter using an ATmega8 microcontroller, offering a cost-effective solution compared to traditional LM3915-based meters. The VU meter uses multiplexing via four transistor-switched LED columns to control 64 LEDs with limited I/O pins, and includes a 5V 7805 regulator, input audio signal conditioning, and minimal noise A/D conversion. The project highlights PCB design considerations, component placement, and programming instructions for the microcontroller to drive the LEDs with PWM for current control.
Parts used in the 2x32 LED VU Meter:
- ATmega8 microcontroller (DIL28PZ 7.5mm socket)
- 64 LEDs (2x32 configuration, 2.5x5mm size)
- 7805 voltage regulator
- Heat sink (cooler) for 7805 regulator
- Transistors for switching LED columns
- Resistors (including adjustable trimmers R1 and R2 for input sensitivity)
- Wire jumpers (2 for LEDs and 16 for LED jumpers)
- Screw terminals or direct wire leads for voltage and signal supply
- PCB with designed tracks for LED fields and components
Lately, when I went deeper into programming, I was fascinated by precise A / D converters in microcontrollers. And so I decided to make a 2×32 LED VU meter with the ATmega8 microcontroller, which can be bought for example in GME for only 34Kc, and so it comes out much cheaper than the LM3915 which also serves as a VU meter, but only for 1×10 LEDs.Perhaps it is strange how I can control the 64 LEDs with I / O pins. This is solved by simply switching 4 columns with LEDs at high speed.
Photo of a VU meter constructed in a non-soldering field:
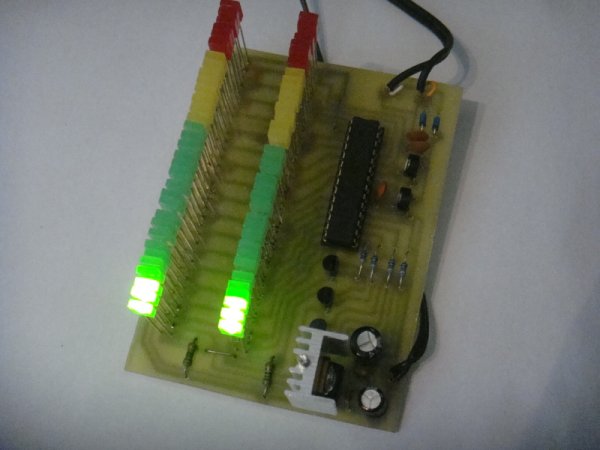
Photo of finished VU-meter:
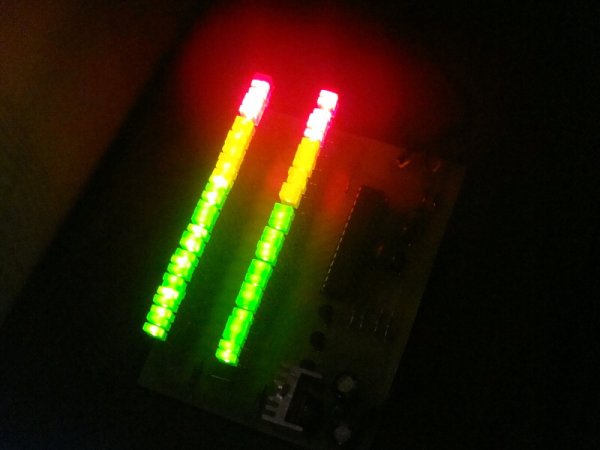
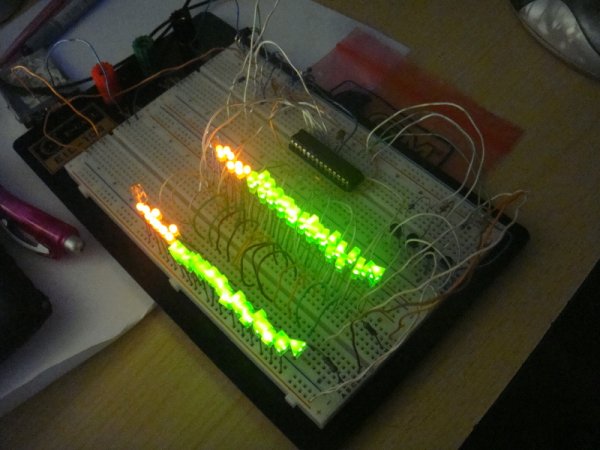
Photo of the finished VU-meter by dark:
Diagram
The circuit diagram is very simple. In the top right is a 5V stabilizer. If you have a directly stabilized 5V 400mA available, you can drop this part, but most of this will be used in amplifiers where we do not have stabilized 5V. The cooler must be placed on the 7805 stabilizer. The size of the chiller is given by the supply voltage, if the power supply is 12V, it will lose up to 3W, and there is still a relatively small cooler (see photo). However, at higher feed voltages, it is better to roll the stabilizer onto the wires and place it on a large cooler.
Below the Schematic Stabilizer, input audio adapters for A / D converters in the microcontroller. Set R1 and R2 trimmers to set the required sensitivity to the input signal.
On the right-hand side are transistors that quickly switch individual LED columns. And on the left are the LEDs themselves. LEDs need not be connected via any resistor due to the internal resistance of the microcontroller which limits the current to the LED to about 80mA, and due to the rapid switching of the 4 LED columns, a PWM modulation will be created to ensure that a current of about 20mA flows into one LED. Below 2x32LED LEDs there are 2 LEDs that are lit continuously and serve as power-on indicators.
In the center is the C3 microcontroller itself, which minimizes the A / D converter noise.
List of parts:
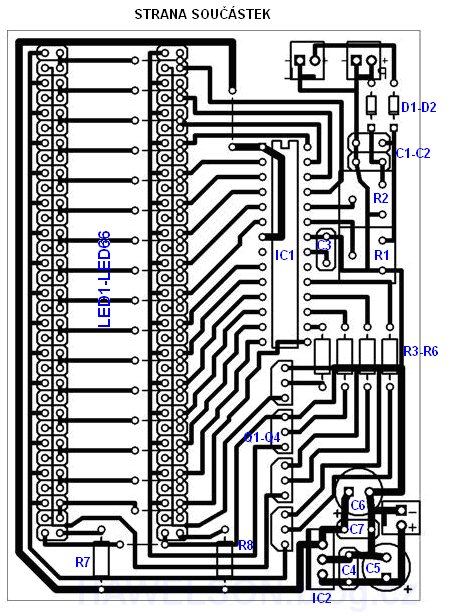
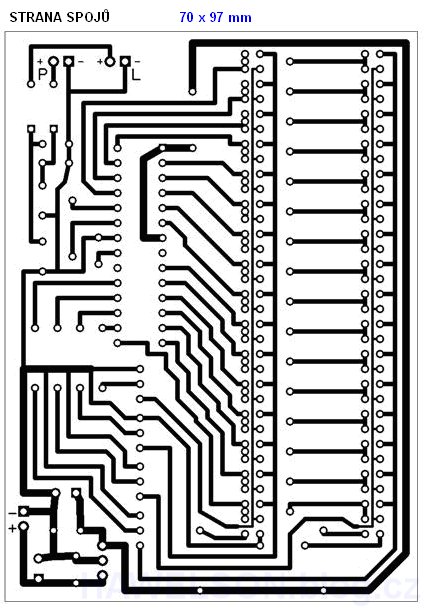
DPS
When making PCBs, we pay attention to LED fields, where copper strips are close to each other, whether bad etching is not where they are to be connected.
When installing, be sure to first install 2 wire jumpers out of the leds and 16 LED jumpers. For PCs, I have long hesitated for what LEDs to create it. Originally I wanted to do it for 5mm LEDs, but the PCB would have to be very long (at 5mm spacing of 33cm in length), so I finally decided to make the PCB for 2x5mm LED, respectively 2.5x5mm. These LEDs are quite cheap to get, and in addition to the LEDs, it can be adjusted to any large LED.
We place the socket (DIL28PZ 7.5mm) on the IC1 slot so that we can easily program the microcontroller and eventually insert it into the PCB. We will not forget to place the cooler on the IC2.
At the place of the voltage and signal supply, we can either put the screw terminals into dps or simply lead the wires directly into the PCB.
PCB component side:
DPS link page:
Programming
For a complete description of the programming, refer to the Programming ATMEL microcontrollers .
So just copy the text below, copy it to the Notepad and save it with the .hex extension (eg VUmetr.hex). Then upload this hex file using PonyProg to the microcontroller.
The source code in C is uploaded HERE , you need to copy the code to the Notepad and save it with the .c or paste it directly into the development environment (avr studio).
The LED flashes at about 100Hz for as little noise as possible but can programmatically increase this frequency to 20kHz, but when you disconnect from the sound source, you hear a gentle whistling in the amplified sound.
Source: j.mp/aPvvO6 VU Meter Circuit files alternative link: atmega8-vu-metre-iki-kanal-64-led.rar