Summary of Use a transistor and an ammeter to measure inductance
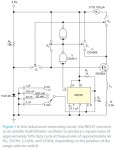
The article explains how to measure inductance using a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). By connecting an inductance and resistance in series to the transistor's emitter and biasing it long enough, the current reaches a maximum correlating to at least five LR time constants. This method utilizes the transistor's property of transferring current from a low-resistance emitter to a higher-resistance collector, effectively allowing the inductance to be gauged through current measurement.
Parts used in the Inductance Measurement Using a Transistor:
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
- Inductor
- Resistor
- Ammeter
Raju Baddi writes: Bipolar junction transistors transfer a current from a lower-resistance emitter to a higher-resistance collector. You can use this property to measure inductance by connecting a series inductance/resistance circuit in the emitter and biasing on the transistor long enough for the current to reach a maximum value that is at least five LR time constants
Read the original here:
Use a transistor and an ammeter to measure inductance