Summary of Charge Pumps Tackle Higher-Voltage Applications
The article explains that charge pumps are circuits designed to produce voltages higher than their supply voltage, providing efficient voltage step-up, step-down, or inversion without inductors. They offer better thermal management and simpler design compared to switching regulators. Linear Technology's LTC3260 and LTC3261 are highlighted as examples of high-voltage inverting charge pumps, offering output currents of up to 100 mA and integrated positive/negative LDO regulators with adjustable output voltages. These devices operate from 4.5 to 32 V input, suitable for high-voltage applications.
Parts used in the High Voltage Inverting Charge Pump Project:
- LTC3260 Inverting Charge Pump with Positive and Negative LDO Regulators
- LTC3261 High Voltage Inverting Charge Pump
- External Resistor Dividers (for voltage adjustment)
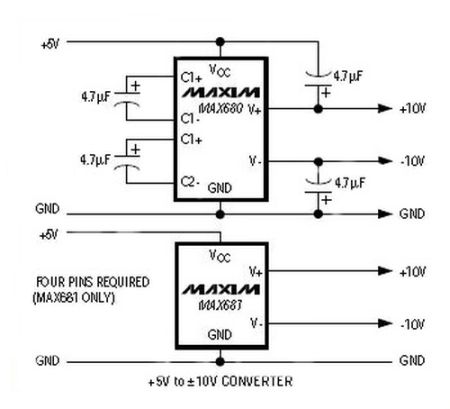
n their most basic form, charge pumps are circuits that generate a voltage larger than the supply voltage from which they operate. Traditionally, charge pumps have been perceived to have limited voltage capability, offering performance that is seen as filling a niche in the range between low-dropout LDOs and switching regulators. Nonetheless, there are benefits that make them attractive for certain applications. For instance, charge pumps deliver higher efficiency with good thermal management and have the flexibility to step up a voltage, step it down, or invert the input voltage. Since they use capacitors to store and transfer energy, charge pumps also are simple to design and do not require an inductor, which can be more costly, has higher output-noise levels, and frequently lowers output-current capability
Typical examples
Linear Technology, for example, has developed two high voltage inverting monolithic charge pump ICs, the LTC3260 and LTC3261, for these applications.¹ The LTC3261 is a high voltage inverting charge pump that can deliver up to 100 mA of output current, while the LTC3260 is an inverting charge pump that includes on-chip both positive and negative LDO regulators that can source up to 50 mA output current each.
The negative LDO post regulator is powered from the inverting charge pump output. The positive and negative LDO output voltages can be adjusted down to 1.2 and -1.2 V, respectively, using external resistor dividers. Both devices operate over a wide input voltage range of 4.5 to 32 V
For more detail: Charge Pumps Tackle Higher-Voltage Applications