Originally developed in Japan and used by Toyota, lean manufacturing has plenty of variations, each promising something else that the other is lacking in. Lean is a vast subject with wide applications across all fields of manufacturing, therefore it is particularly difficult to define it in brief. Nonetheless, it can, in short, be called a series of methods, processes and ideologies that reduce waste, maximize available resources, and cut unnecessary costs to boost productivity and profit margins.
Now that we have access to technology that has revolutionized everything about industrial processes, lean manufacturing has managed to rise up to a whole new level altogether. The basic principles have still remained the same, but the access to so many software and hardware tools have refined lean’s many techniques and principles to perfection.
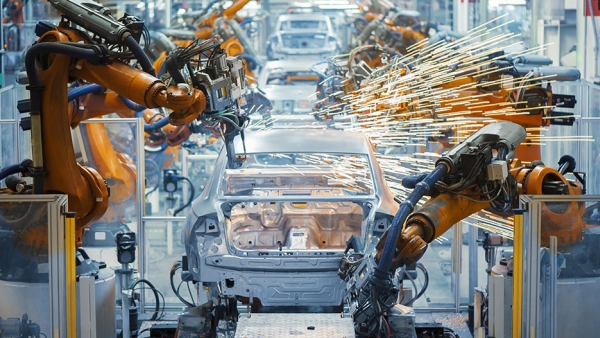
Robotics
Robotics in general have made modern manufacturing safer, faster and more productive, which is by itself, the main goal of lean manufacturing. Therefore, just by installing automated, robotic machines within a production unit, a business would already be on the right path. That however, is not lean manufacturing, but just an essential, technological aspect of the system.
To refine the robotic parts in the production unit with lean manufacturing principles, it would first be necessary to check and see if everything is performing in peak efficiency and requiring minimum effort to do the work it needs to. Some of the common measures which can actually make robotic manufacturing leaner and better can be summarized as follows:
- All robotic equipment should be updated every few years, because technology in the field is developing at a rapid pace
- Whether it’s old or new, regular professional check-ups on every part are essential
- Major robotic equipment that can halt production if it fails should ideally have a replacement ready at all times for emergencies
- Automation via machine learning should minimize the necessity for human intervention
This is just an introduction and a brief guideline regarding how it’s all supposed to be managed, but there is a lot more that needs to be done in order for automated, mechanized production processes to become truly lean.
Achieving that level of perfection is not easy and cannot be expected from anyone who doesn’t have a thorough knowledge of both technology and lean manufacturing, which is precisely what brings us to our next point.
Education: The Basic Requirement for Building a Lean Manufacturing Unit
Knowledge and information are key to modernization, and that’s precisely what has led our modern society to the technological age we live in. Therefore, in order to combine modern engineering and the principles of lean manufacturing successfully, we require the adequate education that teaches professionals how to do so.
The lean manufacturing course provided by an institution like Kettering University Online can provide a graduate with a master’s degree in lean manufacturing. This particular course has been developed in partnership with General Motors (GM), the automotive giant renowned for refining and modernizing lean management from its early days.
Busy professionals do not need to take time off their work to complete a lean manufacturing course and a GRE/GMAT appearance isn’t required either. Online courses can be completed in just one year’s time, but since it is an online course, students are free to take their time, if they need to.
Above everything else, what makes the Master’s degree program in lean manufacturing just perfect is that it combines modern engineering knowledge and concepts with Sigma Six and lean management. As of now, Kettering University’s online lean manufacturing course is probably the only one that is actually able to do this and with a great success rate as well.
After completion of the lean manufacturing course, the workers and the employers will both benefit simultaneously. From the perspective of the employee, they are gaining a Master’s degree in modern lean manufacturing, which can potentially make them invaluable in the core industrial units.
If the employer decides to pay for the training, they are saving on the costs of hiring and training a new workforce without adequate experience, but gaining a more educated and well-equipped version of the workforce they already have. The cost of training and the increased pay scale will be worth it as the production unit will see a significant boost in capacity and will cut down on unnecessary expenses, which in turn will automatically boost profit margins.
What Does Lean Manufacturing and Robotics Have to Do with Employment Rates?
If you take a look around and compare everything as it is, to how it was a century ago, you will notice a trend. A reliance on manual labor has reduced significantly. We do not need horse drawn carts or bulls in the fields anymore.
Can robots replace humans in factories? Well, the answer would have to be a yes, but only as far as repetitive tasks are concerned. There is no denying that robots, especially when guided by modern AI, can work many times harder and produce less errors than human hands do.
As far as basic manual labor is concerned, the answer is yes, robotics can and will inevitably replace it. At the same time, lean manufacturing methods don’t have room for human errors when there is a way to completely eliminate it. That being said, it’s not how it looks, as we will see next.
Both the principles of developing robotic equipment for factories and the principles of lean manufacturing have many things in common, and among them, the safety of the workers is definitely the most prominent one.
A factory that often has to shut down, lose efficiency and suffer the loss of skilled workers due to accidents, is not a factory that has managed to incorporate lean manufacturing effectively. Robotic equipment still needs to be monitored by trained operators in spite of the automation, so there’s actually opportunity for skilled workers in production units more than ever before and the job is much less risky, not to mention it pays a lot higher than minimum wage as well. Contrary to popular belief, robots are only taking over the jobs which humans shouldn’t have to risk their lives for in 2019.