Toshiba Electronics Europe GmbH (“Toshiba”) has launched a new photovoltaic-output photocoupler (“photovoltaic coupler”) housed in a thin SO6L package measuring just 3.84mm × 10mm × 2.1mm, suitable for driving the gates of high-voltage power MOSFETs used to develop a galvanically-isolated solid-state relay (SSR) function.
SSRs are semiconductor relay devices that incorporate a photo-TRIAC, a photo-transistor or a photo-thyristor as the output device. They are generally suitable for applications that require ON/OFF control of large electrical currents such as industrial equipment (I/O relay output for PLCs, inrush current protection in PSUs, battery voltage monitoring in BMS, ground fault detection and more) as well as switching the power and signal lines in instrumentation applications.
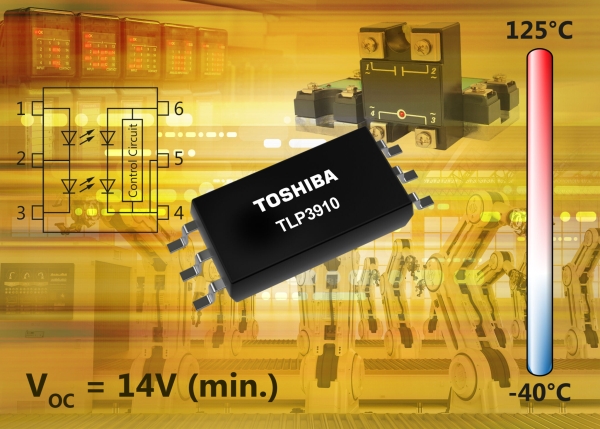
A photovoltaic coupler, such as the new TLP3910, is a photorelay that contains the optical elements but not the MOSFET that performs the high-current switching functions. To easily configure an isolated SSR to handle high-voltage, large-current switching (which photorelays find challenging), designers generally combine a photovoltaic coupler with a MOSFET.
Driving a high-voltage power MOSFET with a gate voltage of 10V or higher, currently requires connecting two of Toshiba’s TLP3906 in series, due to the low open voltage that is around 7V. However, the new TLP3910 has a minimum open voltage (VOC) of 14V, double that of the TLP3906 and, as a result, only a single device is required to drive the gate of a high-voltage power MOSFET. This reduces the part count, thereby improving reliability and saving PCB space and BOM cost.
Improvement to the built-in discharge circuit within the TLP3910 has realized a typical turn-off time (toff) of 0.1ms, about one-third that of the TLP3906 and about one-thirtieth that of the TLP191B. The associated typical turn-on time (ton) is 0.3ms and, together, these ensure high speed operation in end applications.
Read more: TOSHIBA ANNOUNCES NEW PHOTOVOLTAIC-OUTPUT PHOTOCOUPLER
