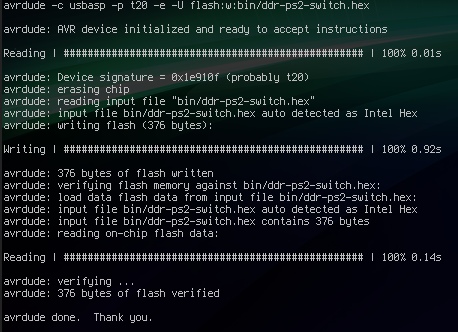
AVR ATtiny4313 in Bascom, GCC and Assembler
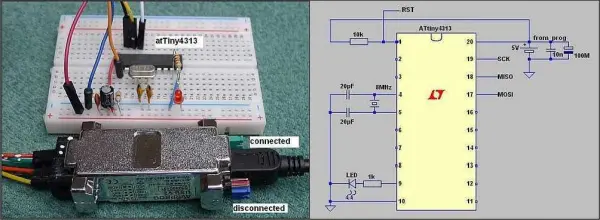
This project explores the functionalities of the AVR ATtiny4313 microcontroller using three different programming environments: Bascom-AVR, GCC, and Assembly language. The focus is on utilizing timers and interrupts to achieve tasks like blinking an LED. Hardware Setup: The project utilizes an ATtiny4313 microcontroller mounted on a breadboard. A crystal oscillator with two capacitors sets the […]
AVR ATtiny4313 in Bascom, GCC and Assembler Read More »